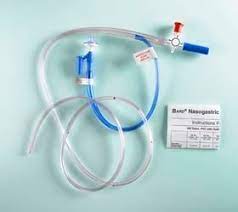
Feeding via a nasogastric (NG) tube requires careful preparation, proper technique, and attention to patient comfort and safety. Here's a general guide on how to feed via an NG tube:
1. Gather Supplies:
- Liquid nutrition formula prescribed by a healthcare provider.
- Syringe or feeding pump (if applicable).
- Clean water or saline for flushing.
- Clean gloves and hand sanitizer.
- Towels or tissues for cleaning spills.
2. Prepare the Formula:
- Follow the instructions provided by the healthcare provider or dietitian for preparing the liquid nutrition formula. Ensure the formula is at room temperature before administering it.
3. Wash Hands and Wear Gloves:
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water before handling the NG tube or feeding equipment. Wear clean gloves to reduce the risk of contamination.
4. Verify Tube Placement:
- Before administering any feedings, verify the placement of the NG tube by checking the pH of gastric aspirate (pH < 5.5 indicates gastric placement) or by obtaining an X-ray confirmation if necessary. Never administer feedings if tube placement is not confirmed.
5. Position the Patient:
- Position the patient in an upright position (preferably sitting or semi-reclined) to facilitate proper flow of the feeding formula into the stomach.
6. Flush the NG Tube:
- Use a syringe to flush the NG tube with saline before and after each feeding session. This helps clear the tube and prevents blockages.
7. Administer the Feeding:
- Attach the syringe or feeding pump to the NG tube.
- Slowly and steadily administer the prescribed amount of liquid nutrition formula into the NG tube. Avoid rapid infusion to prevent discomfort or aspiration.
- If using a feeding pump, set it to the prescribed rate and follow the manufacturer's instructions for operation.
8. Monitor Patient Response:
- Observe the patient for any signs of discomfort, nausea, or intolerance during the feeding.
- Monitor the flow of the feeding formula to ensure it is progressing smoothly and there are no blockages or obstructions in the NG tube.
9. Complete the Feeding:
- Once the prescribed amount of formula has been administered, disconnect the syringe or feeding pump from the NG tube.
- Flush the NG tube again with clean water or saline to clear any residual formula from the tube.
10. Document the Feeding:
- Record the date, time, amount of formula administered, and any observations or patient responses during the feeding session in the patient's medical records.
11. Provide Oral Care:
- After the feeding, provide oral care to the patient to maintain oral hygiene and prevent mouth dryness or discomfort.
12. Dispose of Equipment:
- Dispose of any used syringes, feeding bags, or other equipment according to healthcare facility protocols.
It's essential to follow the specific instructions provided by the healthcare provider or dietitian regarding the type and amount of formula to be administered, feeding schedule, and any special considerations based on the patient's condition. Regular monitoring and communication with the healthcare team are important to ensure the safety and effectiveness of NG tube feeding.
At OneLife Home Healthcare, we understand the challenges individuals face when it comes to meeting their nutritional needs, especially those who rely on enteral feeding through a nasogastric (NG) tube. Our NG tube feeding service is designed to provide compassionate and specialized care for patients in the comfort of their own homes throughout Dubai.
Our Comprehensive Services:
-
Professional Expertise: Our team comprises skilled nurses and healthcare professionals with expertise in enteral NG Tube feeding and tube care. They are dedicated to providing personalized care tailored to each patient's unique needs and medical condition.
-
Patient Assessment: Before initiating NG tube feeding, we conduct a thorough assessment of the patient's nutritional status, medical history, and feeding requirements. This helps us develop a customized care plan that meets the patient's nutritional goals and ensures optimal health outcomes.
-
Tube Insertion and Management: Our trained nurses are proficient in the insertion, placement, and management of NG tubes. Whether it's a new insertion or routine tube care, we prioritize patient comfort and safety throughout the process.
-
Feeding Administration: We ensure the accurate administration of prescribed liquid nutrition formulas or medications through the NG tube feeding . Our nurses follow established protocols to prevent complications and ensure the smooth delivery of feedings.
-
Equipment Provision: We provide all necessary equipment and supplies for NG tube feeding, including feeding pumps, syringes, and tubing. Our team also offers guidance on equipment usage and troubleshooting to patients and caregivers.
-
Education and Support: We offer comprehensive education and training to patients and caregivers on NG tube care, feeding techniques, medication administration, and recognizing signs of complications. Our goal is to empower patients and caregivers to manage tube feeding safely and effectively at home.